Europe is home to some of the world’s oldest cities. Cadiz, a small Spanish port city of about 117,000 inhabitants, is said to be over 9,000 years old. Where there are old cities, there are old neighborhoods and where you find old neighborhoods you find old houses.
Most of these old homes were designed to try to maximize natural ways of heating and cooling. This meant orienting the home in a direction where it received the most sunlight in winter and cool air in summer.
To supplement what they get from nature, most homes typically use traditional boilers and HVAC systems. While these systems might be adequate, in many cases they are not the most energy efficient, cost effective or carbon friendly. Heat pumps are more energy efficient, less costly to run and have a reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional HVAC systems.
A common question owners of old homes have however, is whether heat pumps can be installed in their old home. How suitable are heat pumps for old houses that may have existing HVAC systems like radiators? What would you need to do to retrofit a heat pump system in a situation like this?
What Type of Heat Pump Is Suitable For An Old House?
There are two main categories of heat pumps, namely air source heat pumps and ground source heat pumps. Either can be retrofitted to an existing home.
Retrofitting Air Source Heat Pumps
Air source heat pumps transfer energy from the surrounding air outside to heat or cool a home. This is through an Air-to-air or Air-to-water heat pump.
- Air-to-air heat pumps are air-based systems since they circulate warm or cool air through ducts.
- Air-to-water heat pumps are water-based systems since they regulate temperatures using water pumped through radiators and underfloor heating.
Pros
- Air source heat pumps are less expensive compared to ground source heat pumps. The average cost for air source heat pumps is between £8,000 and £18,000.
- Installation is also much easier and typically requires less space than a ground source system.
- Can be fitted to existing radiators, duct work and hot water tanks.
Cons
- Air source heat pumps are slightly less efficient than ground source heat pumps. This is especially the case for homes in extremely cold climates. One of the main drawbacks of heat pumps is they experience a sharp drop in efficiency when temperatures drop far below zero.
Retrofitting Ground Source Heat Pumps
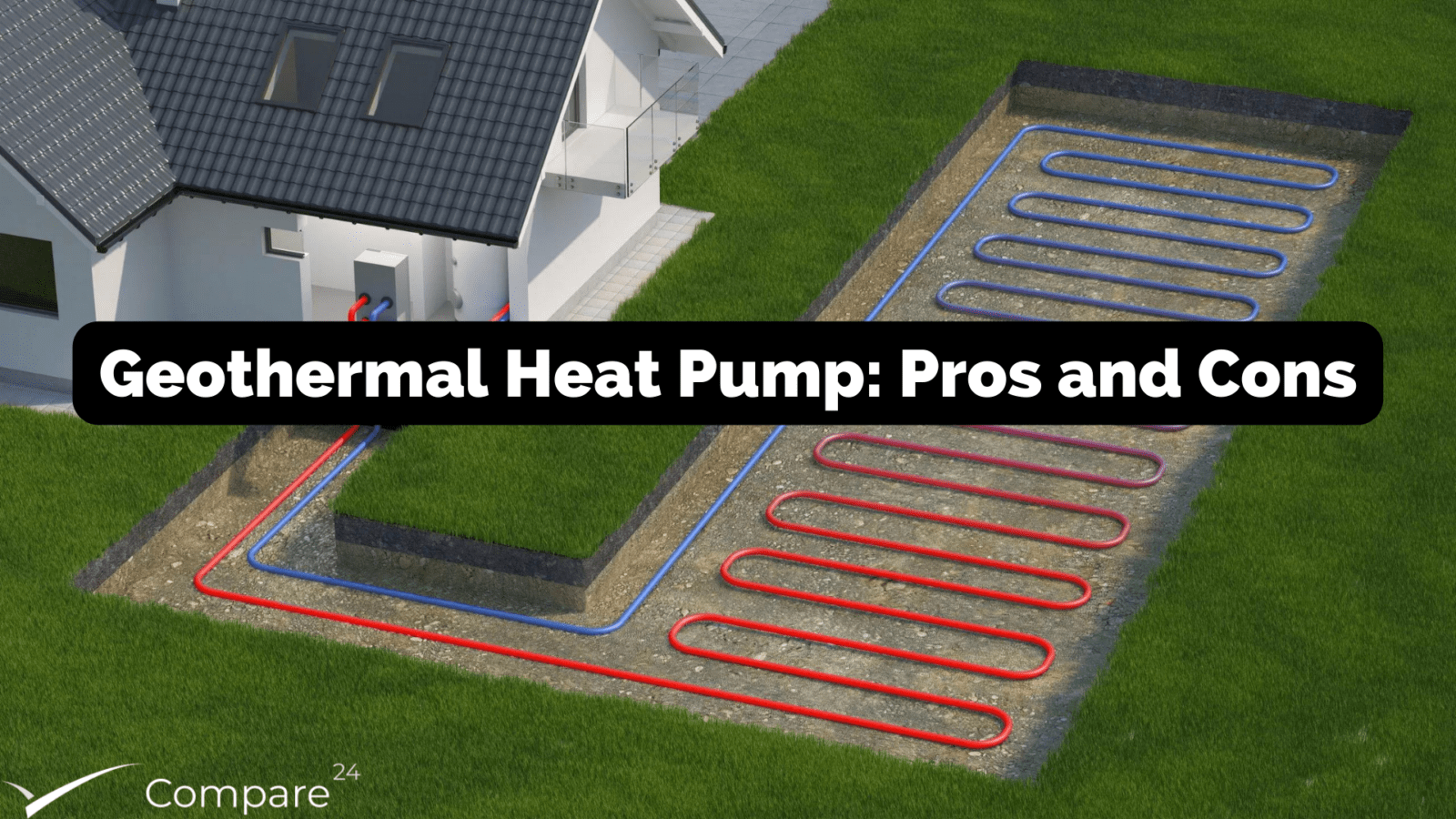
Ground source or geothermal heat pumps draw energy from water circulating in pipes buried underground. There are two variants of a ground source system.
- Horizontal ground source heat pumps lay a network of pipes horizontally or across an area of space underground.
- Vertical ground source heat pumps use vertical boreholes sunk deep into the ground. Vertical pumps are more expensive and used where there isn’t enough space for a horizontal ground source heat pump.
Pros
- Ground source heat pumps are more efficient and will generate more heat compared to an air source heat pump. This is because there is more latent energy in the ground than there is in the air.
- This type of system also has a longer lifespan compared to an air source system.
Cons
- Very high upfront costs. Geothermal systems cost between £20,000 to £35,000.
- The complicated installation of a geothermal system makes it more suited for a new building than for a retrofit.
Verdict
Air source heat pumps are a better option for retrofits. They require much less space for equipment and are not as complicated to install. In contrast, ground source heat pumps require laying a network of piping that takes up a significant amount of space. Generally, geothermal systems are more recommended for new homes.
The much higher cost of a geothermal system is also another factor to consider. If you are unsure of the costs, get quotes here to compare.
Do Heat Pumps Work With Existing Radiators?
Heat pumps distribute heat through a home using radiators, underfloor heating and air ducts. Using heat pumps with existing radiators will likely require some slight adjustments since heat pumps work differently.
Heat pump systems produce and circulate heat slower than traditional heating. Retrofitting a heat pump using existing radiators that were designed with a traditional heating system to a heat pump needs to account for the slower flow rate. This would entail using a larger capacity heat pump.
Designing a heating system for a retrofit needs to consider the size of the home, heating demands, and insulation. From there, an installer will recommend what size heat pump and radiators are required. If the existing radiators are of the right size then the only thing left to work out is the capacity of the heat pump.
If however, the radiators are not of the right size needed to meet the demand, an installer will likely recommend you upgrade your radiators to a larger size or you increase the number of radiators. To get an idea of what this might cost, take our quiz and get a free quote.
The energy efficiency of a home plays a big part in the running costs of a heating system. Insulation will determine just how cost effective a heating system will be.
How Insulated Does A House Need To Be For A Heat Pump?
Insulation should be the first step to retrofitting a new heating system. Any cost savings or improvements in heating efficiency will literally go out the window of a home with poor insulation. Typical signs of poor insulation include:
- Drafts in rooms where doors and windows are closed.
- Mold could be a sign of excessive moisture coming in from a leaky roof for example.
- A higher than average electricity bill.
- Temperature fluctuations that see your home being hotter or colder than average.
- Inconsistent temperatures throughout the house. Some rooms are hotter or colder than others.
Homeowners that improve their insulation see the highest returns when they invest in a heat pump.
How To Insulate An Older Home
The best ways to insulate an existing home is through double glazing, wall and loft insulation. Windows and doors are an easy passage for cold and hot air. Double glazing can reduce your bill by up to £100 a year according to the Energy Saving Trust.
Roofs have the most energy loss in a home. Insulating a loft generally has the most impact on making a home more energy efficient.